DBMS Architecture
Ø A Database Architecture is a representation of DBMS design.
Ø It helps to design, develop, implement, and maintain the database management system.
Ø A DBMS architecture allows dividing the database system into individual components that can be independently modified,
changed, replaced, and altered.
Ø It also helps to understand the components of a database.
Ø A Database stores critical
information and helps access data quickly
and securely. Therefore, selecting the correct Architecture of DBMS helps in
easy and efficient data management.
Ø We choose database architecture depending
on several factors like the size of the database,
number of users, and relationships between the users.
Ø The basic
client/server architecture is used to deal with a large number of
PCs, Web servers, Database servers and other components that are connected via
networks.
Ø DBMS architecture depends upon how users are connected to the database to get
their request done.
Ø There are three types of DBMS
architecture:
o
1-Tier
architecture
o
2-Tier
architecture
o
3-Tier
architecture
 |
| Fig: Types of DBMS Architecture |
A] 1-Tier Architecture:
Ø In this type of architecture, the database is readily available on the client machine, any request made by client doesn’t require a network connection to
perform the action on the database.
Ø This type of system is generally referred
as local database system.
Ø It is the simplest architecture of
Database in which the client, server, and Database all
reside on the same machine.
Ø In this architecture, the database is directly available to the user. It means the user
can directly sit on the DBMS and uses it.
Ø For example, let’s say you want to fetch
the records of employee from the database and the database is available on your
computer system, so the request to fetch employee details will be done by your
computer and the records will be fetched from the database by your computer as
well.
Ø Any changes done here will directly be
done on the database itself. It doesn't provide a handy tool for end users.
Ø It is used for development of the local application, where
programmers can directly communicate with the database for the quick response.
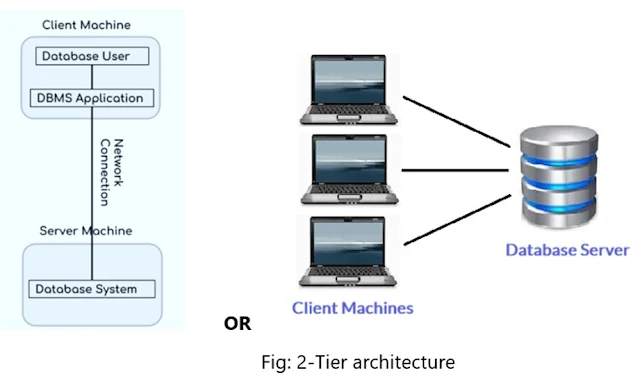
B] 2-Tier Architecture:
Ø The 2-Tier architecture is same as basic
client-server architecture.
Ø Whenever client machine makes a request to access the database present at
server using a query language like SQL, the server perform the request on the
database and returns the result back to the client.
Ø The APIs such as JDBC, ODBC are used for the interaction between server and
client.
Ø The user
interfaces and application programs are run on the client-side.
Ø The server
side is
responsible to provide the functionalities like: query processing and transaction management.
Ø To communicate with the DBMS, client-side
application establishes a connection with the server side.
Ø Client machine and Server machine are
connected with each other through a reliable
network
C] 3-Tier Architecture:
Ø The 3-Tier architecture contains another layer between the client and server.
Ø In this architecture, client can't directly communicate with the server.
Ø 3-Tier database Architecture design is an
extension of the 2-tier client-server architecture.
Ø A 3-tier architecture has the following
layers:
o
Presentation
layer (your PC, Tablet, Mobile, etc.)
o
Application
layer (server)
o
Database
Server
Ø The application on
the client-end interacts with an application server which further communicates with the
database system.
Ø This intermediate
layer acts as a medium for the exchange of partially processed
data between the server and the client. This type of architecture is used in the case of large web applications.
Ø End user has no idea about the existence of the database beyond
the application server. The database also has no idea about any other user
beyond the application.
Ø A 3 Tier Architecture in DBMS
is the most popular client server architecture in DBMS in which the development and maintenance of functional processes, logic,
data access, data storage, and user interface is done independently as separate
modules.
 |
| 3-Tier Architecture |


DBMS architecture is a framework that defines how data is stored, managed, and accessed in a database system. It consists of different levels like the internal, conceptual, and external schema, helping in efficient data management. Understanding DBMS architecture is crucial for optimizing performance and scalability. NAPS2 is a versatile tool that can be useful in document scanning, complementing your DBMS setup with efficient file management.
ReplyDelete