Wireless Media | Unguided Media | Unbouded Media
Ø Unbound
transmission media are the ways of transmitting data without using any
cables.
Ø These
media are not bounded by physical geography.
Ø This
type of transmission is called Wireless communication.
Ø Nowadays
wireless communication is becoming popular. Wireless
LANs are
being installed in office and college campuses. This transmission uses Microwave,
Radio wave, Infra-red are some of popular unbound
transmission media.
Ø Wireless
communication involves no physical link established between
two or more devices, communicating wirelessly.
Ø Electro-magnetic
signals are spread over in the air and are received and interpreted by
appropriate antennas.
Note:
Electro-magnetic waves are special type of wave that can travel without medium.
Ø When an antenna
is attached to
electrical circuit of a computer or wireless device,
it converts the digital data into electromagnetic signals and spread all over
within its frequency range.
Ø The receptor on the
other end receives these signals and converts them back to digital data.
Ø A little part of electromagnetic spectrum can be used for wireless
transmission.
1) Radio Transmission
Ø Radio frequency is easier to generate and
because of its large wavelength & it can travel long
distance.
Ø Radio waves can have wavelength from 1 mm – 100,000 km and have frequency ranging from 3 Hz to 300 GHz.
Ø Radio waves are generated by Radio transmitters
and received by Radio receivers.
Ø Radio stations transmit radio waves using transmitter,
which are received by the receiver installed
in your device. Both transmitter and receiver use antennas
to radiate radio signals.
Ø It can penetrate walls easily, so these waves are widely used for
communication both indoors and outdoors.
Ø Radio waves are omni-directional in nature.
Ø Radio waves at lower frequencies can travel through walls whereas higher RF can travel in straight line and bounce back.
Ø The power
of low frequency waves decreases sharply as they cover long distance. High
frequency radio waves have more power.
Ø Lower frequencies such as VLF, LF, MF bands can travel on the ground up
to 1000 kilometres, over the earth’s surface.
Ø Radio waves of high frequencies are prone to
be absorbed by rain and other obstacles. They use
Ionosphere of earth atmosphere. High frequency radio waves such as HF
and VHF,UHF bands are spread upwards. When they reach Ionosphere, they are
refracted back to the earth.
Ø Types of Radio Waves:
1.
Short Wave-Used in AM radio
2.
VHF(Very High Frequency)-Used in FM radio (TV)
3.
UHF(Ultra High Frequency)-Used in TV
Advantages
·
Offers
mobility
·
Cheaper than
cables
·
Freedom from
Land Acquisition
·
Ease of
Communication in difficult terrains
Disadvantages
·
Insecure
communication(Eavesdropping)
·
Susceptible
to weather condition
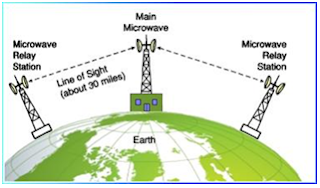
2) Microwave
Transmission
Ø They are used to transmit data without use of cables.
Ø Microwaves are a type of radio waves with
high frequency.
Ø In this parabolic
antennas are mounted on the towers to send the beam to another antenna
KMs away.
Ø Higher is the tower à Greater is the range
Ø Microwaves are in unidirectional in nature.
Ø It is example of Line-of-Sight
transmission
LOS:-Type of propagation that can transmit and
receive data only where transmit and receive stations are in view of each other
without any sort of an obstacle between them. Example Radio, microwave and
satellite transmissions are examples of Line-of-Sight
Ø Microwaves can have wavelength ranging from 1 mm –
1 meter and frequency ranging from 300 MHz to 300 GHz.
Ø It will support bandwidth
upto 1 to 10 Mbps
Ø Attenuation: (Reduction in the strength of a signal.
Sometimes called Loss of signal)-Affected by environmental conditions, antenna size
and strength of signal(Frequency it using)
Ø Microwaves have higher
frequencies and do not penetrate wall like obstacles.
Ø It is used for satellite
communication,navigation,radar,remote sensing and other short distance
communication
Ø They will be encountered by
Eavesdropping(Person sitting in between two antennas and wants to access the
signals by using his own antenna),jamming
Advantages
·
Cheaper than
using cable
·
Freedom from
Land Acquisition rights
·
Ease of
communication in difficult terrains
·
Ability to communicate
over oceans
Disadvantages
·
Insecure
communication(Eavesdropping)
·
Out of phase
signals
·
Susceptible
to weather condition
·
Bandwidth is limited
·
Cost of
design, implementation and maintenance is high
3) Infrared
Transmission
Ø Infrared wave lies in between visible light
spectrum and microwaves.
Ø It has wavelength of 700-nm to 1-mm
and frequency ranges from 300-GHz to 430-THz.
Ø Infrared wave is used for very short-range communication
purposes such
as television and it’s remote, wireless speakers, automatic doors, hand held
devices etc
Ø Infrared travels in a straight line hence it is directional by nature. Because of high frequency range, Infrared cannot cross wall-like
obstacles.
Ø We cannot use infra-red waves
outside a building because sun’s ray contain infrared waves that can interfere with
communication.
Light
Transmission
Ø Highest most electromagnetic
spectrum which can be used for data transmission is light or optical signalling.
This is achieved by means of LASER.
Ø Because of frequency light uses,
it tends to travel
strictly in straight line.Hence the sender and receiver
must be in the line-of-sight.
Ø Because laser transmission is
unidirectional,
at both ends of communication the laser and
the photo-detector
needs to be installed.
Ø Laser beam is generally 1mm wide hence it is a work of precision
to align two far receptors each pointing to lasers source.
Ø Laser works as Tx (transmitter) and
photo-detectors works as Rx (receiver).
Ø Lasers cannot penetrate obstacles such as walls, rain, and thick fog. Additionally, laser beam is distorted by wind, atmosphere temperature, or
variation in temperature in the path.





Fine
ReplyDeleteThanks.. Simple but clear
ReplyDelete