Write a Java program to implement the DES algorithm logic.
HARDWARE
AND SOFTWARE REQUIREMENT:
1. Intel based Desktop PC: - RAM of
512 MB
2. Notepad/Notepad ++
editor
3. Net beans / Eclipse
THEORY:
DES is a block cipher technique which
encrypts data in blocks (64 bit
size), i.e. 64 bits of PLAINTEXT message
goes as the input to DES, which produces 64 bits of CIPHERTEXT message. DES uses a 56 bit key. DES is actually based on the two
fundamental concepts of cryptography: substitution and transposition. It consists of 16 steps called as a rounds. Each round is
responsible for performing the steps of substitution and transposition.
STEP-1:
The 64 bit PLAINTEXT message is given
to an initial Permutation (IP).
STEP-2:
Initial permutation (IP) divides
64-bit PLAINTEXT into two halves ;say Left PLAINTEXT (LPT) and Right PLAINTEXT (RPT).
STEP-3:
Now each LPT and RPT go through 16 rounds of encryption
process.
STEP-4:
In the end, LPT and RPT are re-joined and a
Final Permutation (FP) is performed on
the combined 64-bit block.
STEP-5:
The result of this process produces 64 bit CIPHERTEXT.
SOURCE CODE:
import javax.swing.*;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.KeyGenerator;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.util.Random ;
class DES {
byte[] skey = new byte[1000];
String skeyString;
static byte[] raw;
String inputMessage,encryptedData,decryptedMessage;
public DES()
{
try
{
generateSymmetricKey();
inputMessage=JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null,"Enter
message to encrypt");
byte[] ibyte = inputMessage.getBytes();
byte[] ebyte=encrypt(raw, ibyte);
String encryptedData = new String(ebyte);
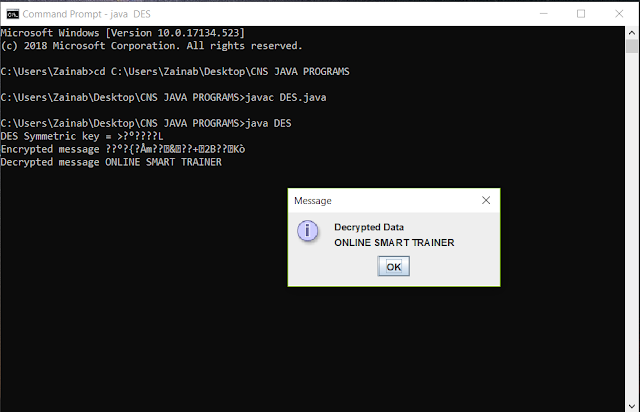
System.out.println("Encrypted message
"+encryptedData);
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,"Encrypted
Data "+"\n"+encryptedData);
byte[] dbyte= decrypt(raw,ebyte);
String decryptedMessage = new String(dbyte);
System.out.println("Decrypted message
"+decryptedMessage);
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,"Decrypted
Data "+"\n"+decryptedMessage);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}
void generateSymmetricKey() {
try {
Random r = new Random();
int num = r.nextInt(10000);
String knum = String.valueOf(num);
byte[] knumb = knum.getBytes();
skey=getRawKey(knumb);
skeyString = new String(skey);
System.out.println("DES Symmetric key =
"+skeyString);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}
private static byte[] getRawKey(byte[] seed) throws
Exception
{
KeyGenerator kgen = KeyGenerator.getInstance("DES");
SecureRandom sr =
SecureRandom.getInstance("SHA1PRNG");
sr.setSeed(seed);
kgen.init(56, sr);
SecretKey skey = kgen.generateKey();
raw = skey.getEncoded();
return raw;
}
private static byte[] encrypt(byte[] raw, byte[]
clear) throws
Exception {
SecretKeySpec skeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(raw,
"DES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, skeySpec);
byte[] encrypted = cipher.doFinal(clear);
return encrypted;
}
private static byte[] decrypt(byte[] raw, byte[]
encrypted)
throws Exception
{
SecretKeySpec skeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(raw,
"DES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, skeySpec);
byte[] decrypted = cipher.doFinal(encrypted);
return decrypted;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
DES des = new DES();
}
}



Comments
Post a Comment